เขามาเห็ฯสูตรและบอกตัวเองว่าเพิ่งสอบไปวันศุกร์ T T......
Announcement
Collapse
No announcement yet.
D.I.Y.ตอน ต่อแอมป์ 40+40 w. ราคาไม่ถึงพัน
Collapse
X
-
อ้าว คุณwizardman ลบไปแล้วยังอ่านไม่เข้าใจเลย
-----------------
อยากจะบอกว่าผม F ฟิสิกส์ อย่างภาคภูมิใจ อ่านสูตรไม่กระดิกเลย
-----------------
เอาแอมป์อมร ตัวล่ะ 480 มาเล่นกับลำโพงaiwa เหลือ ที่บ้าน
ค้นพบอะไรที่แปลกมาก ไม่คิดว่าตัวเองจะลองเรื่องนี้หรอกน่ะเห็นว่ามันไม่น่าสำคัญ
คือ เรื่อง "น็อต"
เล่าอาการก่อน คือชุดนี้มันมีเสียงหึ่งๆ กวนใจตลอดเวลา แล้วแอมป์มันก็สั่น
(แอมป์มันสั่นจริงๆครับ ไม่ใช่ตัวลำโพง ไม่ต้องลำโพงแต่เปิดแอมป์ ถือไว้ในมือ รู้ได้เลยว่าสั่น)
+มีเสียงหึ่งๆ หลุดออกมาตลอดเวลา
ลองเปลี่ยน c หลังไดโอด ลดค่า เพิ่มค่าแล้วก็ไม่หาย ตอนแรกนึกว่าไฟไม่เสถียรเลยเปลี่ยนดู
ลองไปลองมาเห็นน็อตเดิม มันไม่แน่น เลยเอาน็อตเมนบอร์ดมาใช้ ไม่รู้ น็อต เหล็กชุบ หรือน็อตอะลู
ขันให้แน่น
ผลที่ได้ คือเสียงดีขึ้น 40% (โม้ตัวเลขไปงั้นแหล่ะมันวัดเลขไม่ได้หรอก 55+)
แต่เสียงมันดีขึ้นเยอะจริงๆ ครับ เพราะอาการหึ่งมันน้อยลงเยอะ สะงัดขึ้นอีกหนักเลย
สาเหตุอาจจะเป็นเพราะกล่องเป็นโลหะ แล้วเขาเอากราวน์บางส่วนลงกล่องมั้ง(ไม่แน่ใจว่าตรงไหนหาไม่เจอ ไม่รู้ตรงปุ่มvolumeรึเปล่า เดาเอาน่ะ)
ถ้าเปิดแอมป์ไว้แล้วเอามือจับกล่องจะได้ยินเสียงแทรกมาเลย
ว่าแต่ทำไมแอมป์มันสั่นได้ - -?? เพิ่งเคยเจอ
Comment
-
Originally posted by ManiacMaewชุดนี้มันมีเสียงหึ่งๆ กวนใจตลอดเวลา แล้วแอมป์มันก็สั่น
(แอมป์มันสั่นจริงๆครับ ไม่ใช่ตัวลำโพง ไม่ต้องลำโพงแต่เปิดแอมป์ ถือไว้ในมือ รู้ได้เลยว่าสั่น) + มีเสียงหึ่งๆ หลุดออกมาตลอดเวลา
ถ้าเปิดแอมป์ไว้แล้วเอามือจับกล่องจะได้ยินเสียงแทรกมาเลย
ลองไปลองมาเห็นน็อตเดิม มันไม่แน่น เลยเอาน็อตเมนบอร์ดมาใช้ ไม่รู้ น็อต เหล็กชุบ หรือน็อตอะลู ขันให้แน่น
ผลที่ได้ คือ เสียงมันดีขึ้นเยอะจริงๆ ครับ เพราะอาการหึ่งมันน้อยลงเยอะ สะงัดขึ้นอีกหนักเลย
ว่าแต่ทำไมแอมป์มันสั่นได้ - -?? เพิ่งเคยเจออาการของระบบกราวน์ไม่ดีOriginally posted by ManiacMaewถ้าเปิดแอมป์ไว้แล้วเอามือจับกล่องจะได้ยินเสียงแทรกมาเลย
ผมก็คิดแบบนั้นOriginally posted by fenderfreeผมว่าหม้อแปลงหรือเปล่าครับที่สั่น แบบเคลือบมาไม่ดี(หรือไม่ได้เคลือบอะไรเลย)
- หม้อแปลงชุบน้ำยาไม่ทั่วทุกซอกทุกมุม ทำให้ขดลวดภายในเกิดการสั่นขณะทำงาน
- ขายึดหม้อแปลงไม่แนบสนิทกับกล่อง ทำให้เกิดการแกว่งตัวขณะทำงาน
พอขันน็อตยึดให้แน่นขึ้น เลยสั่นน้อยลง
Comment
-
Transformer types by WikipediaOriginally posted by ManiacMaewหม้อแปลงมันมีกี่แบบเนี้ย งง แล้วมันจัดประเภทกันยังไง??
Transformer by Wikipedia
Basic principles
The transformer is based on two principles: first, that an electric current can produce a magnetic field (electromagnetism), and, second that a changing magnetic field within a coil of wire induces a voltage across the ends of the coil (electromagnetic induction). Changing the current in the primary coil changes the magnetic flux that is developed. The changing magnetic flux induces a voltage in the secondary coil.
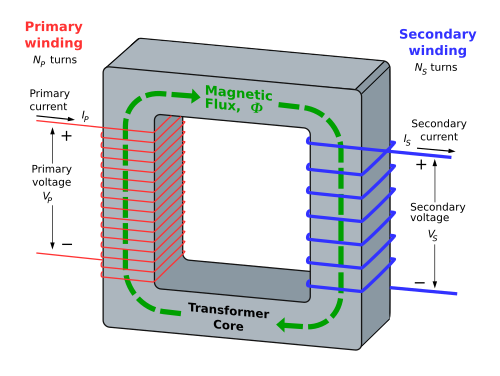
An ideal transformer is shown in the adjacent figure. Current passing through the primary coil creates a magnetic field. The primary and secondary coils are wrapped around a core of very high magnetic permeability, such as iron, so that most of the magnetic flux passes through both the primary and secondary coils.
Leakage flux
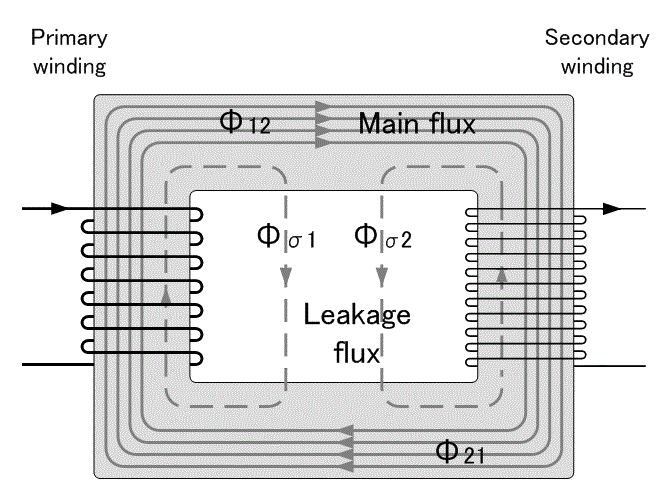
The ideal transformer model assumes that all flux generated by the primary winding links all the turns of every winding, including itself. In practice, some flux traverses paths that take it outside the windings. Such flux is termed leakage flux, and results in leakage inductance in series with the mutually coupled transformer windings. Leakage results in energy being alternately stored in and discharged from the magnetic fields with each cycle of the power supply. It is not directly a power loss (see "Stray losses" below), but results in inferior voltage regulation, causing the secondary voltage to fail to be directly proportional to the primary, particularly under heavy load. Transformers are therefore normally designed to have very low leakage inductance.
However, in some applications, leakage can be a desirable property, and long magnetic paths, air gaps, or magnetic bypass shunts may be deliberately introduced to a transformer's design to limit the short-circuit current it will supply. Leaky transformers may be used to supply loads that exhibit negative resistance, such as electric arcs, mercury vapor lamps, and neon signs; or for safely handling loads that become periodically short-circuited such as electric arc welders.
Air gaps are also used to keep a transformer from saturating, especially audio-frequency transformers in circuits that have a direct current flowing through the windings.
Effect of frequency
The time-derivative term in Faraday's Law shows that the flux in the core is the integral with respect to time of the applied voltage. Hypothetically an ideal transformer would work with direct-current excitation, with the core flux increasing linearly with time. In practice, the flux would rise to the point where magnetic saturation of the core occurs, causing a huge increase in the magnetizing current and overheating the transformer. All practical transformers must therefore operate with alternating (or pulsed) current.
The EMF of a transformer at a given flux density increases with frequency. By operating at higher frequencies, transformers can be physically more compact because a given core is able to transfer more power without reaching saturation and fewer turns are needed to achieve the same impedance. However, properties such as core loss and conductor skin effect also increase with frequency. Aircraft and military equipment employ 400 Hz power supplies which reduce core and winding weight.[38] Conversely, frequencies used for some railway electrification systems were much lower (e.g. 16.7 Hz and 25 Hz) than normal utility frequencies (50 60 Hz) for historical reasons concerned mainly with the limitations of early electric traction motors. As such, the transformers used to step down the high over-head line voltages (e.g. 15 kV) are much heavier for the same power rating than those designed only for the higher frequencies.
Operation of a transformer at its designed voltage but at a higher frequency than intended will lead to reduced magnetizing current; at lower frequency, the magnetizing current will increase. Operation of a transformer at other than its design frequency may require assessment of voltages, losses, and cooling to establish if safe operation is practical. For example, transformers may need to be equipped with "volts per hertz" over-excitation relays to protect the transformer from overvoltage at higher than rated frequency.
One example of state-of-the-art design is those transformers used for electric multiple unit high speed trains, particularly those required to operate across the borders of countries using different standards of electrification. The position of such transformers is restricted to being hung below the passenger compartment. They have to function at different frequencies (down to 16.7 Hz) and voltages (up to 25 kV) whilst handling the enhanced power requirements needed for operating the trains at high speed.
Knowledge of natural frequencies of transformer windings is of importance for the determination of the transient response of the windings to impulse and switching surge voltages.
Comment
-
ขอบคุณครับ แล้วที่คุณkeang พูดถึง เทอรอยด์แบบ r core กับ c core นี้มันต่างกันยังไงเหรอครับ
-----------
อยากโพสต์ ภาพ+ผลเรื่องแอมป์อมรให้ดูแต่เหนื่อยแหล่ะ
เอาออกมาแก้ 2-3รอบแหล่ะ
แก้เรื่องเสียงมัวไม่ได้สักที มัวแบบมีหม่านหมอกมาลงอย่างแรง
เบสบางย่าน ออกย้วยๆ ด้วย
เทสไม่ดีด้วย systemไม่คุ้น ไปเทสกับทีวี+dvdplayer+ไฟล์ ไม่คุ้น สรุปทำไปแยกเสียงไม่ออก
ว่าเปลี่ยนไปยังไง ยกเว้นเรื่องน็อตนั้นแหล่ะที่เห็นชัดมาก
------------
รายงานเพิ่มเติม :
เอาใหม่ - -* ลงกระทู้นี้ล่ะกันเพราะมันเรื่องแอมป์
ต้องเปลี่ยนวิธีทดสอบใหม่ ไรท์เพลงคุ้น หู ที่ฟังมาจน 100รอบแล้วมั้งไปเทส
ทดสอบรอบนี้ เราลองทฤษเดาๆ ใหม่
คราวนี้มีconcept ว่า ระบบกราวน์ดมันไม่ดี เราต้องหาทางกราวน์มันให้ดีขึ้น
โดยประหยัดงบ+ของมีอยู่เล็กน้อย ดึกแล้ว ไม่มีเวลาทำอะไรหนักๆ+เสียงดัง แต่อยากซน
คุณkeang เคยบอกเรื่องกราวน์ดลงกำแพงซีเมนต์ เราเอามาดัดแปลง กราวน์ด ลงขอบหน้าต่างไม้ที่บ้านแทน
เห็นมันมีรูให้ขันน็อตลงได้พอดี
(+ไม้มันน่าจะนำกระแสได้ดีกว่าcement
ความสามารถของกราวน์ด นี้เคยเห็นสูตรแว่บๆ คือเกี่ยวข้องกับค่าความต้านท้านและค่าการเก็บประจุ
ยิ่งต้านทานน้อย+เก็บประจุได้มาก ยิ่งกราวน์ดี เราก็เดาว่าไม้มันน่าจะความต้านทานน้อยกว่าซีเมนต์
เพราะยังไม่เคยเห็นฟ้าผ่า ลงซีเมนต์ เห็นแต่ผ่าลงไม้
+เดาว่าถึงมันจะไม่สัมผัสถึงพื้นก็น่าจะได้อยู่ ผมเคยกราวน์ลงกระถางก็ได้อยู่ อาจจะเพราะมันมีความสามารถเก็บประจุได้ระดับหนึ่งละมั้ง)
สรุปจริงๆ คือเดาแหลก
เอาสายลำโพงเหลือมา
ถอดน็อตตัวหนึ่งออกจากตัวถัง(มีไฟรั่วลงตัวถังใช้ไขควงเข็คไฟเช็คแล้ว)
เอาปลายสายลำโพงที่ปอกแล้วแหย่ไปแล้วก็ขันน็อตยึดมัน
อีกด้านของสายก็ทำเหมือนกัน แหย่ลงไปในรูที่ไม้ขอบหน้าต่าง แล้วเอาน็อตขันยึดไว้
ผล เสียงมันเหมือนจะต่างกันนิดหนึ่ง น้อยมาก จนผมกลัวว่าจะหลอกตัวเองรึเปล่า?
คือเสียงที่ออกมาทางโอบล้อมsurrond มันจะถอยไป เสียงฟังดูสะอาดขึ้นติีดนิด มัวน้อยลงติ๊ดนึง
ฟังยากจริงๆ ถอดเข้าออกฟังอยู่4-5รอบ ได้Last edited by ManiacMaew; 17 Nov 2010, 22:08:22.
Comment
-
คุณkeang เคยบอกเรื่องกราวน์ดลงกำแพงซีเมนต์ เราเอามาดัดแปลง กราวน์ด ลงขอบหน้าต่างไม้ที่บ้านแทน
เห็นมันมีรูให้ขันน็อตลงได้พอดี
(+ไม้มันน่าจะนำกระแสได้ดีกว่าcement
ความสามารถของกราวน์ด นี้เคยเห็นสูตรแว่บๆ คือเกี่ยวข้องกับค่าความต้านท้านและค่าการเก็บประจุ
ยิ่งต้านทานน้อย+เก็บประจุได้มาก ยิ่งกราวน์ดี เราก็เดาว่าไม้มันน่าจะความต้านทานน้อยกว่าซีเมนต์
เพราะยังไม่เคยเห็นฟ้าผ่า ลงซีเมนต์ เห็นแต่ผ่าลงไม้
+เดาว่าถึงมันจะไม่สัมผัสถึงพื้นก็น่าจะได้อยู่ ผมเคยกราวน์ลงกระถางก็ได้อยู่ อาจจะเพราะมันมีความสามารถเก็บประจุได้ระดับหนึ่งละมั้ง)
สรุปจริงๆ คือเดาแหลก
-----------------------
ผิดหมดเลยครับ ถ้าไม่เข้าใจแนะนำให้หาข้อมูลก่อนที่จะโพสครับ จะได้ไม่หลงทาง -*-
Comment
-
ผิดตรงไหนครับบอกหน่อย มั่วไว้เยอะเกิน55+
ตรงที่ผมแน่ใจก็มีเรื่องค่าความต้านท้านของสายกราวน์น่ะ คือ ความต้านน้อยยิ่งดี
ยังมึนๆอยู่ ไปทำเว็บที่มีสูตรหายไปไหนไม่รู้
ความต้านท้านมาก จะทำให้ไฟมันไหลไปไปได้ไม่ดี
เมื่อก่อนก็เคยเถียงอยู่เรื่องกราวน์อันหนึงงเหมือนกันถ้าคุณmilestoneยังจำได้น่ะ
เรื่องที่ ทำกราวน์ดเส้นเดียว แล้วไปลงดิน
กับ แยกกราวน์ดแต่ชุด จากกันแล้วค่อยไปรวบลงดิน
เรื่องนั้นก็ยังไม่ได้หาข้อมูลต่อเลย แต่ก็ยังคิดทฤษฎีเดิมอยู่น่ะ กราวน์ดหลายเส้น ค่าความต้านท้านมันต่ำกว่า
ในทางปฎิบัติ มันย่อมวางระบบกราวน์ยากกว่าอยู่แล้ว
งึมๆ ลองหลายอย่างพร้อมกันเกินไป มึนเอง
Comment


Comment